The tawny nurse shark is a carpet shark living in the Indo-Pacific oceans.

Tawny Nurse Shark Scientific Classification |
|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Chondrichthyes |
| Order | Orectolobiformes |
| Family | Ginglymostomatidae |
| Genus | Nebrius |
| Scientific Name | N. ferrugineus |
Description
These sharks can reach lengths of 10 ft, with a body shaped like a cylinder and a flat head. The nostrils of these sharks have barbels on them. Inside their small mouth, one can observe 29–33 rows of fan-like teeth in the upper jaw and 26–28 in the lower one.
This shark’s dorsal and pectoral fins are angular, while the pelvic fins are narrow and falcate. The caudal fin has a substantial upper lobe that makes up almost 25% of the shark’s total body length. In certain sharks encountered off the coast of Japan and Taiwan, the second dorsal fin is absent, potentially due to the high salinity levels or temperature of those waters.
When looked at from above, the tawny nurse shark is grayish, reddish, or yellowish brown and off-white when seen from below. Juveniles have noticeably white lower eyelids.
Where do they live
Map Of The Tawny Nurse Shark’s Habitat
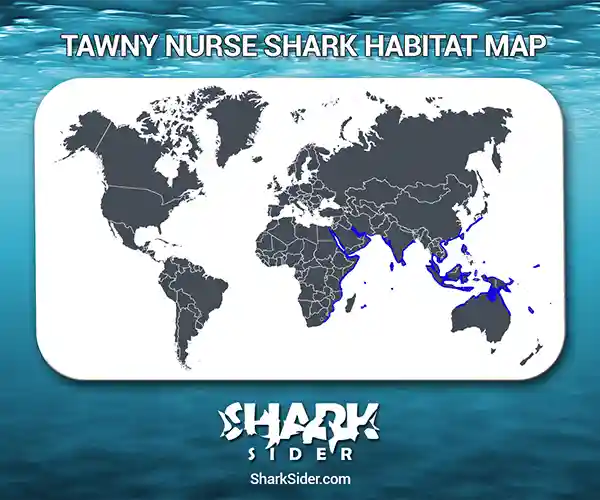
Tawny nurse sharks roam throughout the Indo-Pacific region, having been spotted in Australia, the Chagos Archipelago, China, India, Indonesia, Japan, Madagascar, the Maldives, the Marshall Islands, Mauritius, New Caledonia, Palau, the Philippines, Samoa, Seychelles, South Africa, Southeast Asia, and Tahiti.
They are found inshore at depths of 16–98 ft, living around continental and insular shelves close to beds of seagrass, coral or rocky reefs, or sandy flats.
Behavior
Hunting
These sharks specialize in feeding on octopi, expanding their pharynx to create an intense negative pressure that sucks them in. Other prey they consume include corals, crustaceans, sea urchins, small fish like queenfish, rabbitfish, surgeonfish, squids, and even sea snakes.
Social
As these sharks are often seen stacked on top of each other while resting, they seem pretty social. However, individual specimens have their separate ranges to which they return once a day.
 Reproductive
Reproductive
Female sharks give live birth to 1-2 juveniles about 16 to 31 inches long. While in the womb, these sharks appear to practice oophagy and consume unfertilized eggs for nourishment.
Sexual maturity is observed in males when they are 8 ft 2 inches long, while females do so between 7 ft 7 inches – 9 ft 6 inches. This shark mates between July to August.
Adaptations
This shark can change color to suit its environment, giving it excellent camouflage capabilities.
 Interactions with humans
Interactions with humans
These sharks are quite docile, with captive specimens even being hand-fed. But if provoked, they can deliver a powerful bite thanks to their sharp teeth and suction capabilities.
Tawny nurse sharks are often fished up in their range, though only in Australia are they merely bycatch. They are sold for their meat in other parts of the world.
The IUCN has classified this shark as “Vulnerable” or “VU” due to human activities like fishing with explosions or poisons causing habitat loss. In Australia, it is considered a species of “Least Concern” due to less demand for the shark’s meat.
