Bramble sharks are rare deep-sea sharks living in tropical and temperate waters. It is one of two species in the family, with the other being the prickly shark.
Bramble Shark Scientific Classification |
|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Chondrichthyes |
| Order | Squaliformes |
| Family | Echinorhinidae |
| Genus | Echinorhinus |
| Scientific Name | E. brucus |
Description
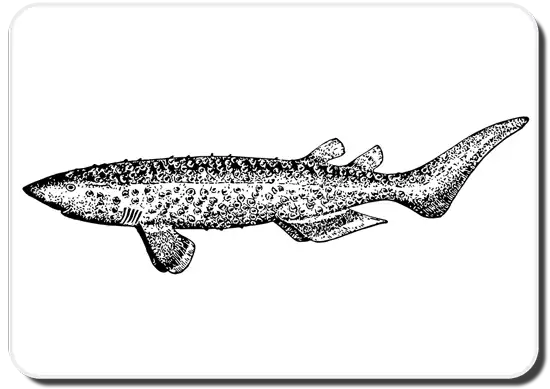
Bramble sharks are around 10 ft long and can reach 440 lb. in weight. They have thick cylindrical bodies with flat heads, round snouts, and five pairs of gill slits. The fifth of these slits is the largest. The nostrils are covered with small skin flaps, and the eyes have third eyelids for protection. Inside the bramble shark’s mouth, one can see rows of knife-like teeth, 20–26 in the upper row and 22–26 in the lower one.
These sharks have short angular fins, long pelvic fins, small dorsal fins, and an asymmetrical caudal fin. Their skin has dermal denticles all over and foul-smelling mucus.
From above, these sharks are brown to black, with a metallic purplish hue, and are much paler from below. Some bramble sharks have red or black marks on them.
Where do they live
This shark is at the same time sparsely seen and widely distributed. Most bramble shark sightings come from the eastern Atlantic and western Indian Oceans, including the British Isles, the Mediterranean Sea, the North Sea, and southern Mozambique. Other places where this shark has been spotted are in the Indo-Pacific, encompassing India, Kiribati, New Zealand, Oman, south Australia, and southern Japan, as well as the western Atlantic, ranging throughout Argentina, Brazil, Louisiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Tobago.
They live close to the ocean floor, around the continental and insular shelves, and slopes at depths of 1,300–3,000 ft. However, they have been spotted in shallow waters at 59 ft and even as deep as 3,983 ft.
Behavior
Hunting
These sharks feed on bony fish like catfish, ling, and lizardfish, crabs, and smaller sharks like spiny dogfish. It is believed that their method of feeding is suctorial.
Reproductive
Viviparous in nature, these sharks give live birth to 15 to 52 pups. Initially, the newborn sharks are 16–20 inches and reach sexual maturity between 4.9-6.9 ft.
Adaptations
Due to their sluggish movements, the mucus covering their body appears to discourage predators from attacking this shark.
Interactions with humans
Bramble sharks are not at all deadly to humans. They rarely interact with them outside of bycatch due to fishing and sometimes being used for meat or liver oil.
The IUCN lists this shark as “Endangered” or “EN”, due to its low growth rate, poor distribution, and falling population due to fishing.
