A medium-sized hound shark, the starry smooth-hound belongs to the Triakidae family. They inhabit waters of the northeast Atlantic Ocean, where it is a native species.
Starry Smooth-Hound Scientific Classification |
|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Chondrichthyes |
| Order | Carcharhiniformes |
| Family | Triakidae |
| Genus | Mustelus |
| Scientific Name | Mustelus asterias |
Description
These sharks grow to lengths of 31-55 inches and have been known to weigh up to 10.5 lbs.
They have a gray or grayish-brown body with tiny white spots scattered on the upper surface, and patches of white on the lower part.
The body is elongated and somewhat lean, with a short head consisting of a blunt snout containing rows of projecting, asymmetric teeth, large eyes and a small mouth whose upper labial furrows are longer than the lower labial furrows.
The dorsal fin in the rear is smaller or sometimes almost the same size as the front dorsal fin. They have medium-sized pectoral fins. The lower and upper lobes of the caudal fin are equally moderate in size, but a notch is present in the upper lobe.
Where do they live
Map Of The Starry Smooth-Hound Shark’s Habitat
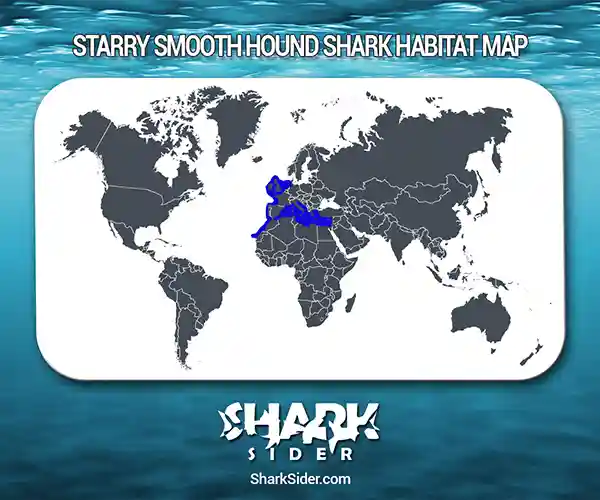
Found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and less commonly in the Mediterranean Sea, the populations of this species range from southern Norway, Scotland, the British Isles, and the North Sea south to Algeria, Morocco, and Western Sahara. There were individual sightings of this species in London’s Thames River in 2021 and the National Marine Park in Plymouth in April 2022.
These sharks prefer sandy and gravel-filled ocean bottoms around continental and insular shelves and islands at depths of 660 ft. They also venture out into 1148.03 feet deep open waters.
Behavior
Dietary
These sharks are nocturnal feeders, their diet comprising bottom-dwelling crustaceans like crabs, lobsters, and mollusks.
Adults even feed on bony fishes and cuttlefish.
Reproductory
These sharks follow a viviparous mode of reproduction where they give birth to live young. The developing embryos feed on the egg yolk and the oviduct’s secretions inside the female’s belly. Litter size consists of 7-15 pups born after a 12-month gestation period. Each pup measures around 12 inches at the time of birth. Both sexes mature sexually at lengths of 31 to 33 inches.
Adaptations
The lean and flexible body of these sharks makes them agile swimmers capable of making very tight turns. This helps in chasing prey quickly. Their lean, flexible body helps them steer in the waters easily, resulting in the tight turns they take when in motion.
Interactions with humans
They are less common in the Mediterranean Sea, often targeted along with another member of their family, the common smooth-hound, for consumption. Hence their numbers in that region have depleted, qualifying them for a Vulnerable status. However, the IUCN lists them as Near Threatened or NT due to their unstable population.
