A species of requiem shark with global distribution, the origins of the milk shark’s name are rather amusing. In India, there was a predominant belief that the meat of this shark helped increase lactation in women. And subsequently, this shark ended up with the name Milk shark.

Milk Shark Scientific Classification |
|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Chondrichthyes |
| Order | Carcharhiniformes |
| Family | Carcharhinidae |
| Genus | Rhizoprionodon |
| Scientific Name | R. acutus |
Description
The milk shark is usually 3.6 ft long, though some specimens off of West Africa are as long as 6 ft. Typically, females are heavier than males. Their bodies are slender, with pointed snouts, round eyes with third eyelids, and furrows around their mouths. A notable feature of these sharks is a series of 7-15 pores on either side of their head, behind their jaws.
Inside this shark’s mouth are 24-25 rows of serrated, oblique teeth in both rows. Milk sharks have a set of broad triangular fins, two dorsal fins with the first being much larger than the second, and an anal fin almost as long as the second dorsal fin.
When looked at from above, this shark appears to be varying shades of gray, while from below, they appear lighter.
Where do they live
Map Of The Milk Shark’s Habitat
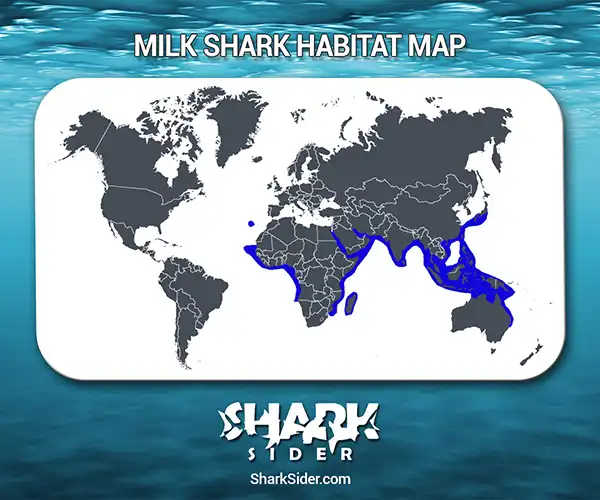
In prehistoric times, the milk shark shared a single border along the Tethys Sea before the continents started to drift. Nowadays, they are more widespread, dotted throughout the world’s oceans.
Milk sharks range from Mauritania to Angola in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, encompassing Madeira and the Gulf of Taranto. At the same time, in the Pacific Ocean, it is seen in China, Indonesia, New Guinea, northern Australia, the Philippines, and southern Japan. In the Indian Ocean, this shark occurs east to South and Southeast Asia, north of the Arabian Peninsula, Madagascar, and South Africa.
Their preferred habitats include the turbid waters of sandy beaches and estuaries from the surf zone to a depth of 660 ft. In Cambodia, milk sharks swimming upstream to freshwater habitats have been reported.
Behavior
Hunting
While the diet of this shark depends on its location, most feed on bony and demersal fish. Milk sharks also consume crabs, cuttlefish, gastropods, octopi, shrimps, and squids.
Migratory
The population of these sharks around KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, peaks around summer, indicating some sort of seasonal migration, though this is yet to be confirmed.
Reproductive
These sharks give live birth to 1-8 pups after a year of gestation, though the typical litter consists of 2-5 pups. Initially, baby sharks are 12.8–19.7 inches long and weigh 0.280–0.772 lbs. They become sexually mature at 2-3 years at varying lengths depending on the region. Milk sharks live for at least 8 years.
Adaptations
Like other requiem sharks, they have a streamlined body letting them swim with ease.
Interactions with humans
 The milk shark is often caught for its meat and as a game fish in Australia, India, Mauritania, Oman, and Senegal. As a result, the IUCN has classified this shark as “Vulnerable” or “VU”, as while it is at risk of exploitation, the shark is capable of sustaining its population better than similar species like the grey sharpnose shark or the Australian sharpnose shark.
The milk shark is often caught for its meat and as a game fish in Australia, India, Mauritania, Oman, and Senegal. As a result, the IUCN has classified this shark as “Vulnerable” or “VU”, as while it is at risk of exploitation, the shark is capable of sustaining its population better than similar species like the grey sharpnose shark or the Australian sharpnose shark.
