The African lanternshark is a member of the family of lanternsharks found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. It is named in honor of Belgian Ichthyologist Max Poll, credited with discovering this species.
African Lanternshark scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Chondrichthyes |
| Order | Squaliformes |
| Family | Etmopteridae |
| Genus | Etmopterus |
| Scientific name | E. polli |
Description
Africanlanternsharks are small, with the maximum recorded length being 24 cm (9.4 in). They have a dark gray, stout body, short gill slits, and large eyes. The underside is blackish below the snout and abdomen, with a broad black mark running above and behind the pelvic fins. There are light-producing photophores along the body and more dark spots over the tail, which is quite long.
In adults, the distance between the pectoral and pelvic fins is slightly lesser than the length of the head. The first dorsal fin originates closer to the pectoral fins than the pelvic fins.
Where do they live
Map Of The African Lanternshark’s Habitat
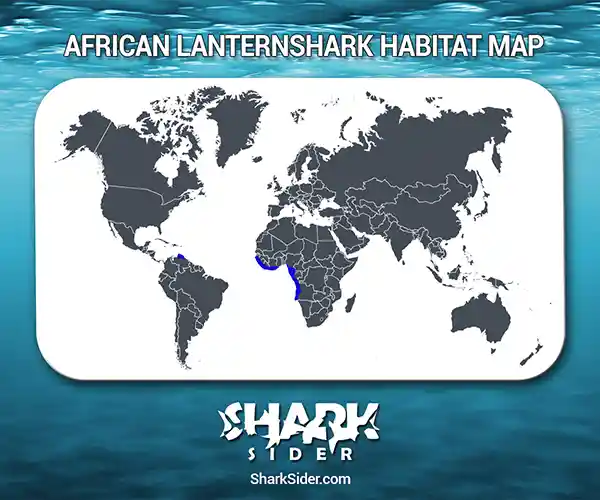
It inhabits the eastern Atlantic along the west coast of Africa, between the latitudes 12°N and 18°S, from Guinea to Angola. It thrives on the continental shelf at depths of 300-1000 m (985-3,281 ft).
Behavior
Dietary
Very little is known about these sharks. Experts presume they have a similar diet to other lanternsharks, feeding on small crustaceans and fish.
Reproductive
There is little information regarding the mating cycle of African lanternsharks. Still, they are assumed to be ovoviviparous like other family members.
Adaptations
They are thought to use their body’s light-producing organs, called photophores, as bait to attract prey and navigate their surroundings.
Human interaction
They are harmless to humans and only caught as bycatch. They are utilized as fishmeal or consumed after drying.
The IUCN has labeled them “Least Concern” or “LC.”
